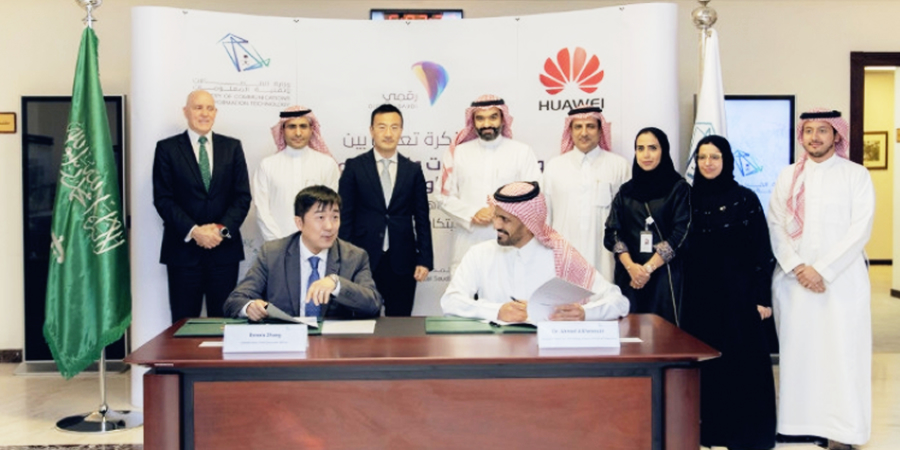
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Communications and Information Technology (MCIT) and Huawei, a leading global ICT solutions provider, have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to enable the national cadre in ICT and promote innovation and entrepreneurship in the sector to push the growth and development of the kingdom, and achieve the goals of Saudi Vision 2030 and the National Transformation Plan 2020.
The MoU also establishes an agreement between Huawei and MCIT to further develop its innovation center in the Kingdom to include Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies designed to support Saudi entrepreneurship.
H.E. Eng. Abdullah Amer Al-Swaha, Minister of Communications and Information Technology, attended the signing ceremony. He was accompanied by Deputy Minister for Technology and Digital Capacities, Dr. Ahmed bin Hamdan Al-Theneyan, Mr. Mark Xue, Vice President of Huawei, Paul Scanlan, CTO, Huawei Technologies and Dennis Zhang, CEO, Huawei Tech Investment Saudi Arabia.
From 2018 to 2020, 1,500 Saudis will undergo training from Huawei in skills related to ICT across the board. Two of the programs, the Future Leaders Program and the National Industrial Training Institute Program will end with full-time employment for every trainee. Huawei will also provide awareness programs to be delivered through VSIC visits as well as its innovative and effective ICT Skill Competition, which should reach an additional 5,000 students and trainees.
In particular, the further joint developments to Huawei’s existing Customer Solution Integration and Innovation Experience Centre (CSIC) facility will focus on the development and utilization of AI and IoT technologies in enabling the Kingdom’s entrepreneurs.
These investments will allow entrepreneurs to use these platforms to further pursue innovation, as well as to train themselves and their organizations for success as digital transformation becomes more comprehensive.
H.E. Eng. Abdullah Amer Al-Swaha commented: “We have successfully signed and carried out significant MoUs with partners in both public and private sectors and non-profit organizations in pursuit of economic diversification, technological advancement and the construction of a knowledge economy. Huawei continues to be an ideal partner in our journey. We are proud of the accomplishments our past MoUs with Huawei have resulted in. We will now strive to accomplish the activities mentioned in this agreement, as it enables us to further empower the Saudi people, and assist them to build a Kingdom that is leading, regionally and globally, when it comes to the frontiers of the digital transformation.”
Mr. Mark Xue, Vice President of Huawei, stated, “We are in a crucial and exciting moment in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s journey towards digital transformation. We have long maintained an approach that is designed to assist and enable the Kingdom’s capabilities and enhance their collective knowledge and expertise in all areas of ICT in order to help them achieve their NTP 2020 and Vision 2030 goals. With robust and comprehensive training programs and expanded facilities that will offer world-class AI and IoT technologies, we are confident that our partnership with the MCIT will be a great service to the Saudi people and the Kingdom as a whole.”
The MoU follows a number of CSR initiatives launched by Huawei in the Kingdom. Huawei brought its global Seeds for the Future training program to Saudi Arabia three years ago in collaboration with the Communications and Information Technology Commission (CITC) in order to develop the next generation of ICT talent.
Huawei’s training center in Riyadh has graduated over 4,000 engineers since it was established in 2006, and more have taken part in educational initiatives at the Huawei Academy with the support of the Saudi Technical and Vocational Training Corporation (TVTC) and Yanbu Royal Commission.
In addition, in 2017 Huawei again collaborated with TVTC and CITC to launch the ICT Skill Competition in Saudi Arabia. The Competition brought together more than 10,285 students from 121 educational institutions across the Middle East, 13 of whom earned a once in a lifetime trip to Huawei’s headquarters in Shenzhen, China, for the final. Six students from Saudi Arabia walked away with Excellence Prizes at the event, and several Saudi institutions were also recognized with awards.