By Dipesh Ranjan, senior vice president and head of Asia Pacific, Mavenir.
Communications service providers (CSPs) in Asia will encounter some familiar issues as the 5G revolution unfolds: an avalanche of goods, tangled infrastructure, and demanding clients. To deal with all of this complexity, CSPs will need to discover ways to deliver seamless experiences across channels while keeping costs down. It will continue to be tough to connect the old with the new, the front office with the back office, and to make vast, complicated enterprises are simpler and more agile. At Mavenir, we believe that key to grasping opportunities with 5G for the telcos in Asia is going to be embracing cloud-based solutions with new business models, interoperability between private and public networks, and the introduction of innovative service models like "pay as you go" based on the open RAN architecture.
All of these scenarios are possible today with software-based solutions for operators, as they start monetizing 5G assets and find new revenue models. There is a wealth of innovation which is happening now on top of the operator networks, and 5G is providing the right opportunity for operators to pounce. CSPs in Asia can utilize the product sets from innovative vendors like Mavenir, such as using our MAVcore cloud-native IMS, to innovate and start becoming a more significant player and moving higher up in the value chain.
5G gives operators the perfect opportunity to add value because now they are not just serving the handsets, they’re serving a multitude of different device types, and have the opportunity to serve across different verticals in different industries. In 2022, we will see catered solutions to serve all these different verticals, indeed in west Australia, Mavenir is working on the deployment of cloud-based private networks for a large scale mining operation in a remote area away from public network services.
We will also see non-traditional players enter the space in Asia. Hyperscalers, for example, will be collaborating with the operators to launch edge services, or system integrators will be innovating to create services that have not existed before. For example, the actual radio hardware piece is now being built by players who have never existed before. And all that is possible because of the advent of open software-based solutions, and if CSPs lose the opportunity to invest and build on that output on top of the solutions in 5G, they have lost the window of opportunity for the next decade as the other big CSPs will have taken the territory.
Let’s next turn our attention to integration with public networks. If you look at the private network market, there has always been a small subset of private service offerings that could be fully enclosed and can be served with a private spectrum. When trying to service larger facilities, let's say you're trying to serve a BMW as an enterprise customer, then there is the need to augment this private spectrum with the public spectrum which comes from operators.
Solutions in 2022 and beyond will need to be designed to offer roaming and network interoperability with existing public networks from operators. At Mavenir we believe the industry will see more scaled private network deployments in small to medium to large enterprises, with the requirement to support not just private on-premises deployments, but the need for hybrid deployments that touch public networks as well.
Another important aspect of open networks applications is that they can be developed by third-party developers. It is these open solutions that have created the platform for new players including hyperscalers like Meta, Microsoft, Google to start offering solutions like private 5G.
However, in the new instance, AWS is solving the problem for the industry and making the model a "pay as you go" which is looking like a consumer offering in terms of financial commitment. Customers, both CSPs and enterprises, which are looking to leverage the public cloud footprint and technology, will now have access to this “click to order” experience from end-to-end secure private network solutions that are also pre-integrated and tested, and at little to no upfront capital expenditure.
This move to cloud and the now possible "pay as you go" business model are providing fundamental shifts in the industry representing both a great opportunity and a threat to traditional communication service providers. At Mavenir, we also foresee the growth of the deployment of intelligent video analytics. Enterprises and telcos can soon deploy AI applications, such as the NVIDIA Metropolis intelligent video analytics solution, and 5G together using an edge server with a converged accelerator. At the end of 2021, we launched our MAVedge-AI intelligent video analytics powered by the NVIDIA Metropolis AI-on-5G platform. This approach delivers flexible, efficient, reliable and secure AI applications over 5G networks.
In terms of use cases, we forecast more need for remote view and analysis due to travel bans and a need to integrate factories and facilities into IoT and the 4th Industrial Age. Global facilities will be connected via a cloud-based network operating seamlessly across private and public networks, just as hyperscalers now connect consumers worldwide and telcos do with integrated messaging services.
We believe that we have insight into this as Mavenir supports over 250 customers with more than 4 billion subscribers; so more than 50% of all subscribers are using Mavenir software on a daily basis.
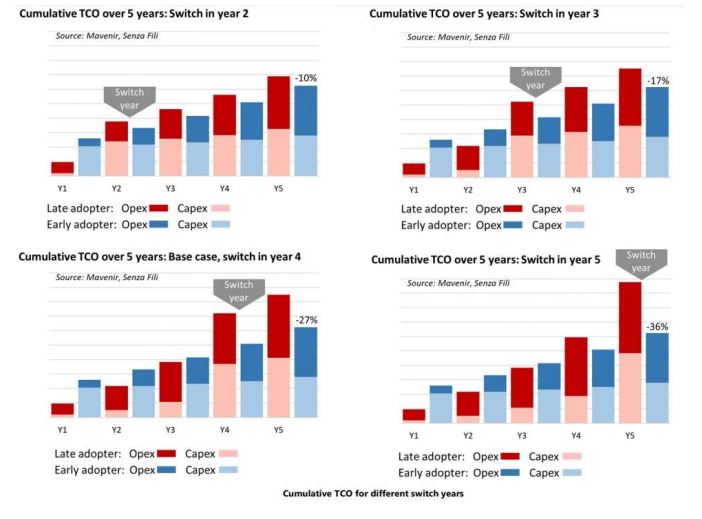
Another issue we see from research is that postponing the adoption of a 5G core increases the total cost of ownership (TCO), Mavenir recently released the findings of a white paper from Monica Paolini at Senza Fili which details how moving to a 5G Core now can reduce TCO by up to 36% over 5 years. The study concludes that mobile network operators (MNOs) can save by moving to a cloud-native converged 5GC with 5G standalone (SA) support as they deploy their 5G access network, instead of relying on legacy EPC technologies and 5G non-standalone (NSA) packet core support. Networks are moving to the cloud, and this is bringing a fundamental shift to the industry.
The GSMA released a comprehensive study of 156 operators worldwide, of which 29% were in Asia, and the results show that 95% of mobile operators recognize the importance of the virtualization of networks. 75% characterize opening network architectures as an “essential process” or "critical step”, and more than half of the executives ranked increased security through visibility into network functions as one of the top reasons to adopt open RAN. Lastly, 94% have plans to deploy open RAN within the next five years. As the world’s only cloud-based end to end telecom solution provider, we at Mavenir think this is a very exciting time for the industry.
We think the year of the tiger in Asia will see greater adoption of cloud-native architecture where applications and services are purpose-built for the cloud model. This open architecture offers easy scaling, hardware decoupling, agility, portability, and resilience across public, private, and hybrid clouds. From an implementation perspective, the legacy model of managing solutions deployments will need to change. The year of the tiger will bring opportunities for CSPs in Asia to take pounce on the opportunities offered by an end to end cloud network, a technology that has earned its stripes.